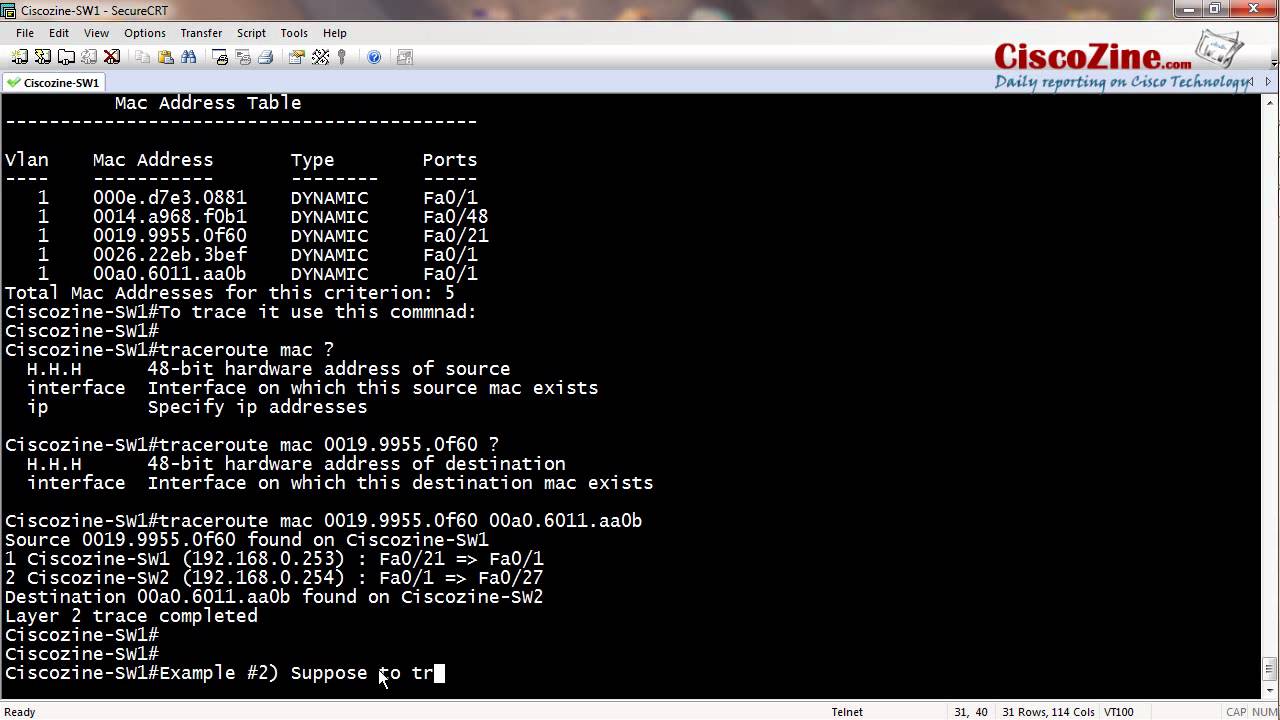
MAC address - Media Access Control address. MAC addresses - hardware addresses that uniquely identifies each node of a network. It is assigned by the vendor or manufacturer and saved to the device memory. According to the OSI model it is a second-level address. Checking MAC Addresses on a Cisco Switch You can check the MAC addresses stored by a Cisco switch by logging into the switch and issuing the command show mac address-table. The addresses are stored in a table called the bridge forwarding table or CAM table.
- Finding Mac Address For Cisco Access Control Module
- Finding Mac Address For Cisco Access Control Devices
- Finding Mac Address For Cisco Access Control Router
- Finding Mac Address For Cisco Access Control Software
If you have a big network with multiple Access Switches connecting to the core switches or routers then tracing a device like a PC or a laptop for troubleshooting or security purposes is one of those tasks that you often end up doing. This is not a difficult task but can certainly be time consuming.
Lets start with an IP address on hand. If you have an IP address on hand quickly ping and check if the device is pingable. If yes, then simply logon to one of your core switches or routers and do a simple sh ip arp
Core1# sh ip arp 192.168.1.15
Setting up a new Access Point remotely on a cisco 2960 switch and need to find the IP address so I can configure it. I'm not seeing the mac address of the access point in my DHCP server. I do see it when I run 'show mac address-table', but it does not display when I run 'show arp'. Show mac address-table include ab12.cf34.aa21. The output will tell you the port of the connected device, e.g.: ab12.cf34.aa21 DYNAMIC Fa0/2. If Fa0/2 is a trunk, go to that switch and follow the steps above, until you find the access port where the host with that MAC address is connected to.
Finding Mac Address For Cisco Access Control Module
Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface
Internet 192.168.1.15 22 0000.1111.1111 ARPA Vlan1
From the above you know the MAC Address of for the device:
IP Address : 192.168.1.15
MAC Address : 0000.1111.1111
Finding Mac Address For Cisco Access Control Devices
Now, do a show mac-address command on the core switch or router. This will show the interface to which it is connected or through which it is learned.
Core1# sh mac-address-table address 0000.1111.1111
Legend: * – primary entry
age – seconds since last seen
n/a – not available
vlan mac address type learn age ports
——+—————-+——–+—–+———-+————————–
Supervisor:
* 1 0000.1111.1111 dynamic Yes 10 Te1/1
This indicates that the device is either connected to the port or though another switch which is connected to the interface. Looking at this, it is very likely that this is a uplink (TenGigabit Ethernet link) to another Distribution or Access switch.
Sometimes, the output might show as follows [note the Po1]
Legend: * – primary entry
age – seconds since last seen
n/a – not available
vlan mac address type learn age ports
——+—————-+——–+—–+———-+————————–
Supervisor:
* 1 0000.1111.1111 dynamic Yes 10 Po1
This indicates that there is a etherchannelis being setup. So do a 'show etherchannel' command to find the phsycial ports that are paired.
Core1# show etherchannel summary
Flags: D – down P – bundled in port-channel
I – stand-alone s – suspended
H – Hot-standby (LACP only)
R – Layer3 S – Layer2
U – in use f – failed to allocate aggregator
M – not in use, minimum links not met
u – unsuitable for bundling
w – waiting to be aggregated
Number of channel-groups in use: 6
Number of aggregators: 6
Group Port-channel Protocol Ports
——+————-+———–+———————————————–
1 Po1(SU) – Te1/1(P) Te2/1(P)
This shows the ports Te1/1 or Te2/1 as a source through which the address is learnt.
Now, do a 'show cdp neighbors' to show the directly connected devices.
Core1# sh cdp neighbors

Capability Codes: R – Router, T – Trans Bridge, B – Source Route Bridge
S – Switch, H – Host, I – IGMP, r – Repeater, P – Phone
Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID
Access1 Ten 1/1 129 R S I WS-C6509 Ten 1/1
That tells you, it is the Access switch 1 that is connected to Te1/1 and not the device itself.

Now, log onto the Access switch and do a 'show mac-adddress-table' command for the MAC address and that should show the interface to which it is connected
[NOTE: unless it is a distribution switch to again there are a bunch of Access switches connected in which case, you need to go through the whole procedure as above again]
Access1# show mac-address-table 0000.1111.1111
Finding Mac Address For Cisco Access Control Router
vlan mac address type learn age ports
——+—————-+——–+—–+———-+————————–
Supervisor:
* 1 0000.1111.1111 dynamic Yes 10 Gi1/24
As you can see which port the device is connected and on which switch.
Now do a 'show interface' command to show the port details.
Finding Mac Address For Cisco Access Control Software
Access1>sh int gigabitEthernet 1/24
GigabitEthernet1/24 is up, line protocol is up (connected)
Hardware is C6k 1000Mb 802.3, address is xxxx.xxxx.xxxx (bia xxxx.xxxx.xxxx)
MTU 1500 bytes, BW 1000000 Kbit, DLY 10 usec,
reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255
Encapsulation ARPA, loopback not set
Keepalive set (10 sec)
Full-duplex, 1000Mb/s
…..
…
..
.
There you go you found the device switchport that you tried to trace!!!
If you're new here, you may want to subscribe to my RSS feed. Thanks for visiting!
